One-Pot Three Component Synthesis of some 8-Benzeloxy-5-{2-[N-(2-Chloro-Quinolin-3yl -Methelene)-Hydrazino]-Thiazole-4-yl}c-1H-Quinoline 2-Ones
Keywords:
Multicomponent synthesis, quinoline, thiazole, maxium yields, room temperature conditionsAbstract
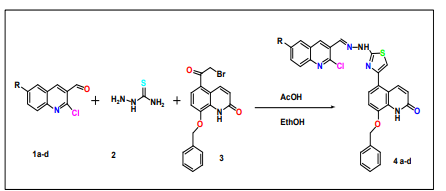
Synthesis of a new series of 8-Benzeloxy-5-{2-[N-(2-chloro-quinolin-3ylmethelene)-hydrazino] is investigated in this work. One-pot multicomponent synthesis of -thiazole-4-yl-1H-quinoline-2-one was achieved by condensation of substituted 2. Chloroquinoline thiosemicarbazide, -3-carbaldehydes, and 8-benzyloxy-5-(2-bromo-acetyl)-1H-quinolin-2-one.
References
S. Raut, A Tidke, B. Dhotre, P.M. Arif, “Different strategies to the synthesis of indazole and its derivatives: A review”, Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry, Vol.17, Issue.4, pp.363-404, 2020.
T.S. Choudhare, D.S. Wagare, V. Jagrut, P. Netankar, “Three Component One-Pot Synthesis of Novel 8-Benzyloxy-5-{2-[N?-(1, 3-Diphenyl-1 H-Pyrazol-4-Ylmethylene)-Hydrazino]-Thiazol-4-yl}-3, 4-Dihydro-1 H-Quinolin-2-Ones”, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, Vol.43, Issue.2, pp.1-8, 2022.
N.D. Parmar, “Design, Synthesis, Characterization and Biological evaluation of (4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl) piperazin-1-yl)(substitutedphenyl) methanones as antimicrobial agents”. World Scientific News, Vol.122, pp.193-205, 2019.
J.H. Lange, P.C Verveer, S.J. Osnabrug, G.M. Visser, “Rapid microwave-enhanced synthesis of 4-hydroxyquinolinones under solvent-free conditions”, Tetrahedron Letters,.Vol.42, Issue., pp.1367-1369, 2001.
D.O. Bates, T.G. Cui, J.M. Doughty, “VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma”,. Cancer research, Vol.62, Issue.14, pp.4123-4131, 2002.
Hennequin, L.F., et al., “Design and structure? activity relationship of a new class of potent VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors”, Journal of medicinal chemistry, Vol.42, Issue.26, pp.5369-5389, 1999.
V. Caprio, “A novel inhibitor of human telomerase derived from 10H-indolo [3, 2-b] quinoline. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, Vol.10, Issue.18, pp.2063-2066, 2000.
L.J. Guo, C.X. Wei, J.H. Jia, L.M. Zhao, Z.S. Quan “Design and synthesis of 5-alkoxy-[1, 2, 4] triazolo [4, 3-a] quinoline derivatives with anticonvulsant activity”, European journal of medicinal chemistry, Vol.44, Issue.3, pp.954-958, 2009.
Y. Shivaraj, “Design, synthesis and antibacterial activity studies of novel quinolinecarboxamide derivatives”, Journal of the Korean Chemical Society, Vol.57, Issue.2, pp.241-245, 2013.
M.V. De Souza, K.C. Pais, C.R. Kaiser, M.A. Peralta, M.L.Ferreira, and M.C Lourenco, “Synthesis and in vitro antitubercular activity of a series of quinoline derivatives”, Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, Vol.17, Issue.4, pp. 1474-1480, 2009.
S.S. Dave, A.M. Rahatgaonkar, “Syntheses and anti-microbial evaluation of new quinoline scaffold derived pyrimidine derivatives”, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, Vol.9: pp.S451-S456, 2016.
F. Clemence, “4-Hydroxy-3-quinolinecarboxamides with antiarthritic and analgesic activities”, Journal of medicinal chemistry, Vol.31, Issue.7, pp.1453-1462, 1988.
S.R. Pattan, C.S.Suresh, V.V.K. Reddy, “Synthesis and antidiabetic activity of 2-amino [5`(4-sulphonylbenzylidine)-2, 4-thiazolidinedione]-7-chloro-6-fluorobenzothiazole”, Indian Journal of Chemistry -Section B, Vol.44, Issue.11,pp.2404-2408, 2005.
A. Prajapati, V.P. Modi, “Synthesis and biological evaluation of some substituted amino thiazole derivatives”, Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, Vol.55, Issue.2, pp.240-243, 2010.
T.K., Spencer, G.I. Georg, J. Aube, “A convenient preparation of 2?[15N]?amino?4, 6?dimethoxypyrimidine”, Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, Vol.28, Issue.4, pp.433-436, 1990.
G. Wells, T.D. Bradshaw, M.F.G. Stevens, “Antitumourbenzothiazoles. Part 10: the synthesis and antitumour activity of benzothiazole substituted quinol derivatives”, Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters,. Vol.10, Issue.5, pp.513-515, 2000.
S. Rollas, S. GunizKuçukguzel, “Biological activities of hydrazone derivatives”, Molecules, Vol.12, Issue.8, 12(8), pp. 1910-1939, 2007.
A.A. Chavan, N.R. Pai, Synthesis and antimicrobial screening of 5-arylidene-2-imino-4-thiazolidinones. Arkivoc, Vol.16, pp.148-155, 2007.
Eicher and S. Hauptmann, The Chemistry of Heterocycles. Wiley VCH. 2003.
B.S. Dawane, S.G. Konda, V. Kamble, S. Chohan, “Multicomponent one-pot synthesis of substituted Hantzschthiazole derivatives under solvent free conditions”, E-Journal of Chemistry, Vol.6(S1): pp.S358-S362, 2009.
J. Vijaya, “Synthesis, characterization and anthelmintic activity (perituma-posthuma) of fluoro substituted benzothiazole for biological and pharmacological screening”, International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences, Vol.1, Issue.3, 2010.
K.S. Kim, S.K. David, K.R. Webster, “Discovery of aminothiazole inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 2: synthesis, X-ray crystallographic analysis, and biological activities”, Journal of medicinal chemistry,.45(18), pp.3905-3927, 2002.
G Luo, “Development of integrase inhibitors of quinolone acid derivatives for treatment of AIDS: an overview”,Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, Vol.10, Issue.11, pp.1046-1057, 2010.
Z. Xu, X.F. Song,Y.Q. Hu, “Azide-alkyne cycloaddition towards 1H-1, 2, 3-triazole-tethered gatifloxacin and isatin conjugates: design, synthesis and in vitro anti-mycobacterial evaluation”. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Vol.138, pp.66-71, 2017.
Y.L. Fan, “Antiplasmodial and antimalarial activities of quinolone derivatives: an overview”. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Vol.146, pp.1-14,2018.
C Sharma, “Insight view on possible role of fluoroquinolones in cancer therapy. Current topics in medicinal chemistry”, Vol.13, Issue.16, pp.2076-2096, 2013.
V. Sharma, R. Das D.K. Mehta “Recent insight into the biological activities and SAR of quinolone derivatives as multifunctional scaffold”,. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, Vol.59, pp.116674, 2022.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





