Effects of Contaminants on the Rheological Properties of Oil Based Muds
Keywords:
Plastic viscosity, yield point, gel strength, drilling, salt, cementAbstract
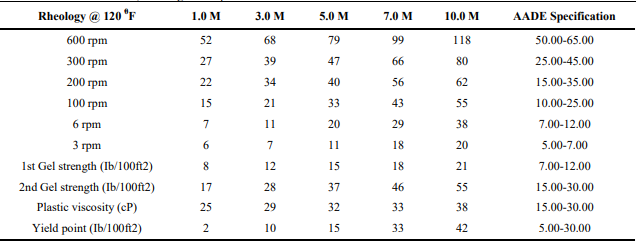
Oil based muds obtained from the Niger Delta area of Nigeria were contaminated with various concentrations of salt and cement contaminants. Molar concentrations of 1.0 M, 3.0 M, 5.0 M, 7.0 M and 10.0 M of salt as well as those of cement were introduced into 10.0 Liters of the Oil based mud respectively with the molar concentrations corresponding to 10.0%, 30.0%, 50.0 %, 70.0% and 100.0 % of the contaminated mud system. The Rheological properties of the contaminated Oil base muds were determined with the use of a Fann Model 35 Viscometer. Results obtained showed that the Plastic viscosity and the Gel strengths of the Oil based mud contaminated with 30.0 % salt solution were within American Association of Drilling Engineers (AADE) specification while only 10.0 % of the cement contaminated Oil based mud fell within AADE specification in terms of Plastic viscosity and Gel strengths, also 50.0 % of both salt and cement contaminated Oil based mud were within AADE specification in terms of Yield point. The salt used as contaminant was sodium chloride (NaCl) while the cement used was portland cement with chemical composition 3CaO.SiO2, 2CaO.SiO2, 3CaO.Al2O3 and 4CaO.Al2O3FeO3 and the rheological properties (Plastic Viscosity, Yield point and Gel strengths) generally increased with increase in concentration of the contaminants however results obtained from Pearson’s correlation coefficient analyses showed that the rate of increase was higher with the cement contaminant indicating that cement has a more devastating effect on the mud properties compared to salt.
References
A. R. Ismail, A. Aftab, Z. H. Ibupoto, “The Novel Approach for theEnhancement of Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluids by Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube, Nanosilica and Glass Beads,” Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, pp 264–275, 2016.
P. Cousin, F. Bertrand, B. Herzhaft, “Rheological Behavior of Drilling Muds, Characterization Using MRI Visualization,” Oil & Gas Science and Technology. Rev IFP, Vol. 59. 23-29, 2004.
N. Awele, “Investigation of Additives on Drilling Mud Performance with, Tonder Geothermal, drilling as a Case Study,” M.S. Thesis, Esbjerg, Aalborg University, 2014.
S. I. Reilly, Z. Vryzas, V. Kelessidis, “First-Principles Rheological Modelling and Parameter Estimation for Nanoparticle-Based Smart Drilling Fluids,” Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 38: 1039–1044, 2016.
J. T. Srivatsa, M. B. Ziaja, “An Experimental Investigation on Use of Nanoparticles as Fluid Loss Additives in a Surfactant-Polymer Based Drilling Fluid Presented at the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Bangkok,” IPTC-14952-MS. https://doi.org/10.2523/ IPTC-14952-MS, 2012.
Z. Peter, A. Rob, E. L. Ane, B. G. L. Erik, “Reservoir geology of the Utsira Formation at the first industrial-scale underground CO2 storage site (Sleipner, area North Sea),” Geological Society, London, Special Publications, p. 165-180, 2004.
J. Nasser, A. Jesil, T. Mohiuddin, M. Al Ruqeshi, G. Devi, S. Mohataram, “Experimental investigation of drilling fluid performance as nanoparticles,” World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 3(03):57, 2013.
M. Amani, M. Al-Jubouri, A. Shadravan, “Comparative study of using oil-based mud versus water-based mud in HPHT fields,” Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development 4 (2):18–27, 2012.
C. S. Ibeh, “Investigation on the effects of ultra-high pressure and temperature on the rheological properties of oil-based drilling fluids,” 55-60, 2009.
O. F. Joel, E. C. Ndubuisi, L. Ikeh, “Effect of cement contamination on some properties of drilling mud. In: Nigeria Annual International Conference and, Exhibition Lagos, Nigeria,” DOI: http://dx.doi. org/10.2118/163023-MS, 2012.
J. Lee, A. Shadravan, S.Young, “Rheological Properties of Invert Emulsion Drilling Fluid under Extreme HPHT Conditions,” Presented at the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition, 6-8 March 2012.
M. C. Onojake, T. N. Chikwe, “Rheological Properties of Some oil based muds used in Reservoirs in the Niger Delta, Nigeria,” Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences 25: 39-44, 2019.
F. Carole, I., Catalin, A. P. William, “Theoretical and Practical Models for Drilling Waste Volume Calculation with Field Case Studies,” pp 75-110, 2010.
K.V. Dyke, “Drilling fluids. Rotary drilling series (unit II). Austin, TX,” The University of Texas, 2000.
S. R. Smith, R., Rafati, A. S. Haddad, “Application of Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles to Enhance Rheological and Filtration Properties of Water Based Muds at HPHT Conditions,” Colloid Surface, 361–371, 2018.
American society of mechanical engineers (ASME), “Drilling fluids processing,” Handbook shale shaker committee, Gulf publishing company, 10-40, 2005.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





