Spectroscopic Analysis of Conducting Polymeric Material
Keywords:
Polymeric Material, Complex, Polyaniline and Polyaniline-Zink complexAbstract
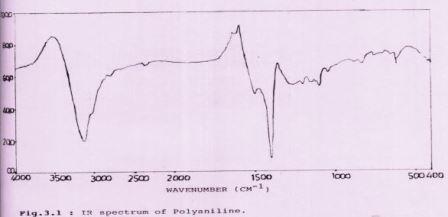
Spectroscopic analysis of conducting polymeric material helps to reveal valuable information about the complex formation of metal(Li,Zn,Al etc.)with ligand i.e. polymer(Polyaniline,Polyethylaniline,Polymetylaniline,Polypyrrolidone etc.).Various spectroscopic technics may be used in this manner such as Infra Red spectroscopy,X-ray Diffraction technich ,UltraViolet spectroscopy etc.In this paper Infra Red spectroscopy and X-ray Diffraction technich have been used to analyse the complexation and conducting behaviour of the polymeric material which can be used in rechargeable batteries.Infrared spectroscopy deals with various bands which correspond to the charecteristic functional groups and bonds present in polymeric substances .In other words Infrared spectoscopy has been used for assigning the binding sites in metal : polymer complexes.A critical comparision of the structurally important IR absorption bands of each polymer and that of its complexes with Zn(II) and Al (III) metal ion has been reported. In the X-ray analysis of polymers the diffraction spots are board and diminish rapidly with increasing diffraction angle .X-ray spectroscopy, like optical spectroscopy is based upon measurement of emission absorption scattering fluorescence and diffraction of electromagnetic radiations. Such measurements provide much useful information about the composition and structure of matter6,7,8 To study the structural properties of polymeric material X-ray diffraction measurements are performed through the interaction of X-ray the structure of the compound may be thoroughly investigated. The X-ray diffraction theory based on single crystals of low- molecular weight substances is not applicable in the explicit treatment of polymer samples. There are a few studies in this direction 9, 10, 11 X-ray diffraction formulas are sorted to kinds, A and B as follow – (A) X-ray diffraction intensity by an infinitely large crystal. (B) X-ray diffraction intensity by a finitely large crystal. X-ray studies of Polymers and their complexes have been done.
References
J.Lingane,Chem.Rev.,29,1(1941)
Youn Chaol on ,Park yong Woo. Hanguk Multi.Hakh-oechl,Ungyong Mulli, 2(3), 256- 60(Korean)(1989).
C. Herold ,R.Yazami,D.Billaud,Terre (France)
W.John Albery, Zheng Chem., Benjamin R.Horrocks, Andrew R. Mount and Peter. J.Wilson, David Bloor Andew T. Monkmann ,C.Michal Elliot ,Fabradar Chem. Soc.88, 247-259(1989)
Bruno Scrosati, solid state ionic devices, 18-23 July 131-133(1988)
H.A. Liebhatsky,H.G. Preiffer,E.H.Winslow and P.D.Zemany,X-Rays,Electrons and Analytical Chemistry John Wiley and Sons (NewYork), (1972).
Bertin EP, Introduction to X-ray Spectrometric Analysis, Plenum press (NewYork), (1978).
R. Jenkins, R. W. Gouid and D. Gedeke,Quantitative X-ray spectrometry marcel Dekker, (NewYork),(1981).
L.G. Wallner, Monatsh, Chem 79, 86 (1948).
L.G. Wallner, Monatsh, Chem 79, 279 (1948).
B.K. Vainshtein, Diffraction of X-ray by chain Molecules ,Eisovier, Amsterodam, 257 (1966).
K. Kaji and I. J. Sakuraka, Polym. Sci. ,Polym Phys.,Ed. 12,1491(1974).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





