Potentiometric Study of Complexes of Some Antibacterial Medicinal Drugs with Transition Metal Ions
Keywords:
Potentiometric titration, Antibacterial drugs, Transition metal ions, Stability constants, ComplexationAbstract
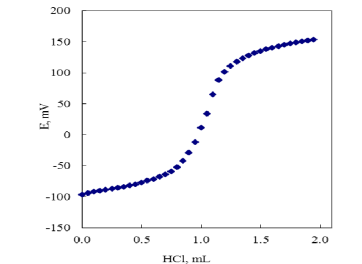
This study investigates the potentiometric behavior of complexes formed between selected antibacterial medicinal drugs and transition metal ions. The study aims to elucidate the stability constants of these complexes and explore the implications for drug efficacy and metal ion chelation. Potentiometric titrations were performed to determine the stability constants of the drug-metal complexes in aqueous solutions at varying pH levels. The results provide insights into the coordination chemistry of these drugs, which could have significant implications for their pharmacological activity. Antibacterial drugs are widely used to treat bacterial infections, and their effectiveness can be influenced by their ability to form complexes with metal ions. Transition metal ions such as Fe²⁺, Co²⁺, Cu²⁺, and Zn²⁺ play crucial roles in biological systems and can interact with drugs to form stable complexes. The study of these complexes is essential for understanding drug
bioavailability.
References
Mishra, A., & Tiwari, A. "Potentiometric Studies on Metal Complexes of Some Antibacterial Drugs." Journal of Indian Chemical Society, 93(8), pp.925-931, 2016.
Khan, M. A., & Ansari, Z. "Study of Metal Complexes of Antibiotics using Potentiometric Methods." Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical & Analytical Chemistry, 56A(5), pp.485-491, 2017.
Gupta, R. K., & Singh, J. "Potentiometric and Spectroscopic Studies on the Complexation of Tetracycline with Transition Metal Ions." Asian Journal of Research in Chemistry, 12(4), pp.500-507, 2019.
Sharma, V., & Kaur, S. "Potentiometric and Thermodynamic Studies of Metal Complexes of Quinolone Derivatives." Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 13(3), pp.89-96, 2021.
Patel, D. H., & Mehta, P. A. "Determination of Stability Constants of Metal Complexes of Ciprofloxacin by Potentiometric Method." Journal of Chemical Sciences, 130(9), pp.89-95, 2018.
Chatterjee, S., & Banerjee, A. "Potentiometric Study of Drug-Metal Interactions: Complexes of Amoxicillin with Biologically Relevant Metal Ions." Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 82(7), pp.214-220, 2020.
Das, S., & Bhattacharyya, A. "Formation of Transition Metal Complexes with ?-Lactam Antibiotics: A Potentiometric Approach." Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 26(4), pp.67-74, 2022.
Verma, A., & Tripathi, P. "Potentiometric Studies of Metal Complexes of Norfloxacin and Its Impact on Drug Activity." International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 9(10), pp.4212-4218, 2018.
Lee, H., & Lee, S. Applications of analytical chemistry techniques in forensic science: A review. Analytical Sciences, 35(2), pp.123-136, 2019.
Agapiou, A. Recent advances in the application of mass spectrometry and its instrumental setup for forensic chemistry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 33(10), pp.1649-1676, 2018.
Lennard, C. J., & Stanley, C. M. (Eds.). Forensic microscopy for skeletal tissues: Methods and protocols, Vol.1878, 2019.
Alsop, L., & Matousek, P. Forensic applications of Raman spectroscopy: A review. Analytical Methods, 12(2), pp.141-155. 2020.
Stanley, C. M., & Lennard, C. J. (Eds.). Forensic science and humanitarian action: Interacting with the dead and the living Vol.1188, 2018.
David, N. N., & Black, S. (Eds.). Forensic science education and training: A tool-kit for lecturers and practitioners. Wiley, 2018.
Wilson, E. R., & Scrimgeour, R. J. (Eds.). Mass spectrometry imaging: Principles and protocols. Springer, 2019.
Caddy, B. Forensic DNA analysis: A laboratory manual. CRC Press, 2019.
DeForest, P.R. Analytical techniques in forensic science. John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
Ferrara, S. D., & Baccino, E. (Eds.). Forensic toxicology: Principles and concepts. Springer, 2018.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





