Synthesis and Characterization of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via Chemical Co-Precipitation
Keywords:
Characterization, Nanoparticles, Synthesis, Application, MetalsAbstract
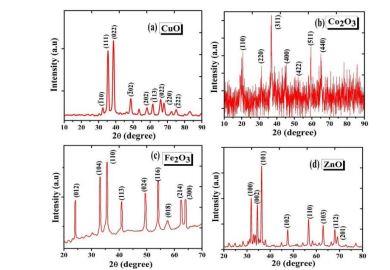
The purpose of this research is to investigate the possible uses of synthesized and characterized metal oxide nanoparticles in a range of industries, including electronics, catalysis, and environmental remediation. The remarkable qualities of metal oxide nanoparticles, such as their large surface area, catalytic activity, and adjustable electrical and optical properties, make them very intriguing. Because of these qualities, they are perfect for many technical and industrial uses. This research used a chemical co-precipitation method to create oxide nanoparticles of zinc, copper, iron, and cobalt. Synthesized nanoparticles show potential for application in environmental cleanup, sensor development, and other high-tech fields due to their customized features.
References
Besenhard, Maximilian & Lagrow, Alec & Hodzic, Aden & Kriechbaum, Manfred & Panariello, Luca & Bais, Giorgio & Loizou, Katerina & Damilos, Spyridon & Cruz, M. & Thanh, Nguyen & Gavriilidis, Asterios. Co-Precipitation Synthesis of Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with NaOH: New Insights and Continuous Production via Flow Chemistry. Chemical Engineering Journal. 399. 125740, 2020. 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125740.
Durukan, M.B., Yuksel, R. and Unalan, H.E. Cobalt oxide nanoflakes on single walled carbon nanotube thin films for supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 222, pp.1475-1482, 2016.
Fadli, Ahmad & Komalasari, Komalasari & Adnan, Arisman & Iwantono, Iwantono & Rahimah, & Addabsi, Adela. Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles via Co-precipitation Method. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 622. 012013, 2019. 10.1088/1757-899X/622/1/012013.
Hui, Beh & Salimi, M. Nabil. Production of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Co-Precipitation method with Optimization Studies of Processing Temperature, pH and Stirring Rate. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 743. 012036, 2020. 10.1088/1757-899X/743/1/012036.
Jagtap, S.V., Tale, A.S. and Thakre, S.D. Synthesis by sol gel method and characterization of Co3O4 nanoparticles. Int. J. Res. Eng. Appl. Sci, 7, pp.1-6, 2017.
Kumar, N., Yu, Y.C., Lu, Y.H. and Tseng, T.Y. Fabrication of carbon nanotube/cobalt oxide nanocomposites via electrophoretic deposition for supercapacitor electrodes. Journal of materials science, 51(5), pp.2320-2329, 2016.
Kandpal, N.D. & Sah, Nitesh & Loshali, R. & Joshi, R. & Prasad, J. Co-precipitation method of synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research. 73. pp.87-90, 2014.
Riaz, Saira & Bashir, Mahwish & Naseem, Shahzad. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Modified Co-Precipitation Method. Magnetics, IEEE Transactions on. 50. pp.1-4, 2014. 10.1109/TMAG.2013.2277614.
Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M., Naderi, H.R., Karimi, M.S., Ahmadi, F. and Pourmortazavi, S.M. Cobalt carbonate and cobalt oxide nanoparticles synthesis, characterization and supercapacitive evaluation. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, Vol.28, Issue.2, pp.1877-1888, 2017.
Rami, Jitesh & Patel, Chirag & Patel, Mansish. Synthesis and Characterization of Selected Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. ITM Web of Conferences. 65, 2024. 10.1051/itmconf/20246504006.
Salavati-Niasari, M., Khansari, A. and Davar, F. Synthesis and characterization of cobalt oxide nanoparticles by thermal treatment process. InorganicaChimica Acta, 362(14), pp.4937-4942, 2009.
Wadekar, K.F., Nemade, K.R. and Waghuley, S.A. Chemical synthesis of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) nanoparticles using Co-precipitation method. Res J Chem Sci, Vol.7, Issue.1, pp.53-55, 2017.
Zhang, Q., Park, K., Xi, J., Myers, D. and Cao, G. Recent Progress in Dye?Sensitized Solar Cells Using Nanocrystallite Aggregates. Advanced Energy Materials, Vol.1, Issue.6, pp.988-1001, 2011.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





