Analysis of Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Parameters of Rawal and Khanpur Dams
Keywords:
Dams, Microbial Identification, Heavy Metals, Health Risks, Water Quality, RawalpindiAbstract
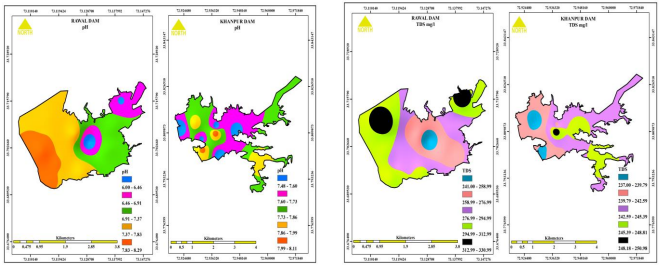
Water is an essential natural resource for every living organism thus water quality is an important parameter that cannot be overlooked. This study was conducted in order to perceive the water quality and microbial characterizations of Rawal and Khanpur Dams that supply water to Rawalpindi. Water samples were collected at five points of the Rawal and Khanpur dams from March to May 2019 with the furthest sampling points upstream situated at the Korang and Haro rivers entering into Rawal and Khanpur dams. Water samples were obtained from various sites for physicochemical, microbiological examination, and heavy metals analysis. Different physico-chemical constraints together with pH, Total dissolved solids (TDS), Conductivity, Chlorides (Cl-), Florides (F-), hardness, and alkalinity were measured by standard methods. Atomic absorption spectroscopy was used to assess heavy metal concentrations such as arsenic (As), chromium (Cr), iron (Fe), lead (Pb), and nickel (Ni). The Standard Plate Count (SPC) method was employed to calculate the total viable count and total coliform count in water tasters. Different bacteriological colonies were extracted from water samples and identified using various biochemical assays, including Gram staining. The results indicated that several physicochemical parameters including pH, TDS, Cl-, F-, COD, and heavy metals such as As, Cu, and Fe were within World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines. While conductivity readings in a few samples were above the WHO permitted limits. Results of both dams in different periods varied greatly which indicates the temporal and spatial variations. Most of the water parameters of both dams were within the acceptable limits provided by the World health organization (WHO). Water was found safe to utilize for drinking purposes except for a few locations of Rawal dam where microbial counts were found high. Further studies on water quality are required to ensure the supply of safe drinking water to consumers. The study provided a holistic approach to understanding the impacts of toxic water on the health of organisms.
References
M.K. Ahmed. S. Islam. S. Rehman. M.R. Haque. M.M. Islam. Heavy metals in water, sediment, and some fishes of Buriganga River, Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research. Vol.4, pp.321-332, 2010.
R. Ullah. R.N. Malik. A. Qadir. Assessment of groundwater contamination in an industrial city, Sialkot, Pakistan. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. Vol.3, Issue. 12, pp.429-446, 2009.
N. Ejaz. U.A. Naeem. M.A. Shahmim. A. Elhai. N.M. Khan. Environmental impacts of small dams on agriculture and groundwater development: A case study of Khanpur dam, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences. Vol.10, pp.45-50, 2012.
American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed, Washington, DC. 2005.
American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed, Washington, DC. 2005.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 3015 microwave-assisted acid digestion of aqueous sample and extracts. In: Test methods for evaluating solid waste, 3rd ed, US EPA, Washington. 1995.
A. Jamil, T. Khan, F. Majeed, D. Zahid, Zabiullah. Drinking water quality characterization and heavy metal analysis in springs of Dewan Gorah, District Palandri, Azad Jammu, and Kashmir, Pakistan. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Geology. Vol.9, Issue.3, pp.33-39, 2018.
P. Edimeh, I.S. Eneji, O. Oketunde, R. Shaato. Physico-chemical parameters and some heavy metals content of rivers Inachalo and Niger in Idah, Kogi State. Journal of Chemical Society. Nigeria. Vol.36, Issue.1, pp.95-101, 2011.
M.O. Aremu, O. Olaofe, P.P. Ikokoh, M.M. Yakubu. Physicochemical characteristics of a stream, well, and borehole water sources in Eggon, Nasarwa state, Nigeria. Journal of Chemical Society. Nigeria. Vol.36, Issue.1, pp.131-136, 2011.
M. Soylak. F.A. Aydin. S. Saracoglu. L. Elci. M. Dogan. Chemical analysis of drinking water samples from Yozgat. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies. Vol.11, Issue.2, pp.151-156, 2002.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





