Determination of Heavy Metals (Ag+, Cd2+ and Pb2+) Using FAAS and ISE in Soil Samples of Selected Eastern Hararghe Area
Keywords:
Soil, Heavy Metal, Ion Selective Electrode, Environmental Contamination, Atomic Absorption SpectroscopyAbstract
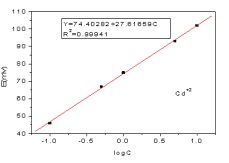
Soils are composed of mineral constituents, organic matter (humus), living organisms, air, and water, and it regulates the natural cycles of these components. Heavy metal is the metallic chemical element that has a relatively high density and it is toxic and poisonous at low concentrations. This work designed to determine and analyses the distribution of heavy metals present in the soil samples obtained from newly closed landfill at Haramaya, Awaday and Harar areas. The amount of heavy metals (Cd+2, Pb+2, Ag+) present in the soil sample was determined using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) and ion selective electrode. In the study the level of Pb2+ determined in various province of eastern Hararghe, was above the acceptable values of WHO guideline (< 0.01 ppm). However, the concentration of Cd2+ and Ag+ were within permissible values of WHO guideline (<3 and 0.05-2 ppm respectively). The method developed using ISE further validated its precision by relating the results obtained using AAS. The average percent of recovery for the ISEs when compared to AAS was 76.7%, which is largely due to differences in the fundamental response characteristics of the two methods, as ISEs only detect the free metal, whereas AAS detects total concentration.
References
A. A. wodaje Adidis, “Determination of heavy metal concentration in soils used for cultivation of Allium sativum L . ( garlic ) in,” Cogent Chem., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–12, 2018.
S. D. Keesstra et al., “The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations sustainable development goals,” Soil, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 111–128, 2016.
K. K. and G. N. C.VIJAYA BHASKAR, “Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water Samples of Certain Locations Situated Around Tumkur , Karnataka , India,” E-Journal Chem., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 349–352, 2010.
H. I. Mustapha, J. Bala, and D. Sunday, “HEAVY METALS IN AGRICULTURAL SOILS IN NIGERIA?: A REVIEW,” Arid Zo. J. Eng. Technol. Environ., vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 593–603, 2017.
T. Ihl et al., “Concentración de elementos tóxicos en suelos del área metropolitana de la Ciudad de México: análisis espacial utilizando kriging ordinario y kriging indicador,” Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient., vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 47–62, 2015.
H. I. Mustapha, J. Bala, and D. Sunday, “HEAVY METALS IN AGRICULTURAL SOILS IN NIGERIA?: A REVIEW,” Arid Zo. J. Eng. Technol. Environ., vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 593–603, 2017.
D. E. Güven and G. Akinci, “Comparison of Acid Digestion Techniques To Determine Heavy Metals In Sediment And Soil Samples,” Gazi Univ. J. Sci., vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 29–34, 2011.
R. A. Wuana and F. E. Okieimen, “Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils?: A Review of Sources , Chemistry , Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation,” Int. Sch. Res. Network, ISRN Ecol., vol. 2011, 2011.
M. Alushllari and N. Civici, “Determination of Lead Accumulation By Leaves of Different Vegetation, Grow in Soil Pollution,” Eur. Sci. J., vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 1857–7881, 2014.
R. Singh, N. Gautam, A. Mishra, and R. Gupta, “Heavy metals and living systems: An overview,” Indian J. Pharmacol., vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 246–253, 2011.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.





